CySky: Enumeration
CySky Notes Enumeration & Exploitation
Enumeration & Exploitation
Challenges
- Python 1 (easy) n/i
- Python 2 (easy)
- Python 3 (medium)
- Binary 1 (medium)
- Binary 2 (hard)
- Timebomb (easy) n/i
- Bytes (easy) n/i
Main Tools
The main tools used in these challenges:
- uncompyle (Python 2, Python 3)
- CyberChef (Python 2)
- gdb (Binary 1, Binary 2)
- Ghidra (Binary 1, Binary 2)
Python 2
Given a compiled Python script, find a password to authenticate the program.
Tools used
- uncompyle6
- CyberChef
Process
- Download
PYTHON2.pyc - Run uncompyle6 (up to Python 3.12)
- The uncompiled script is here:
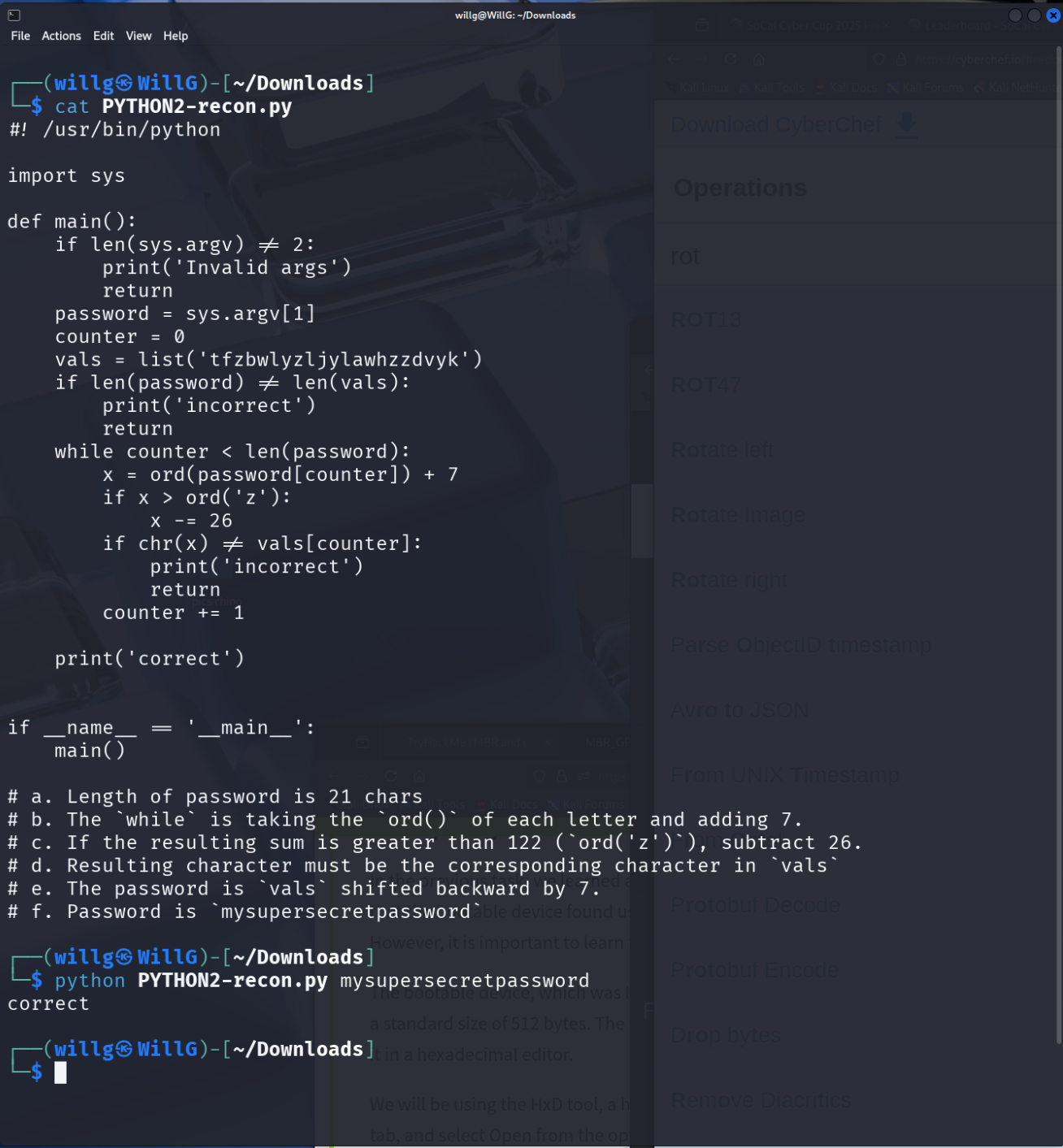
- Use CyberChef with
ROT13, and manually set “Amount” to-7:
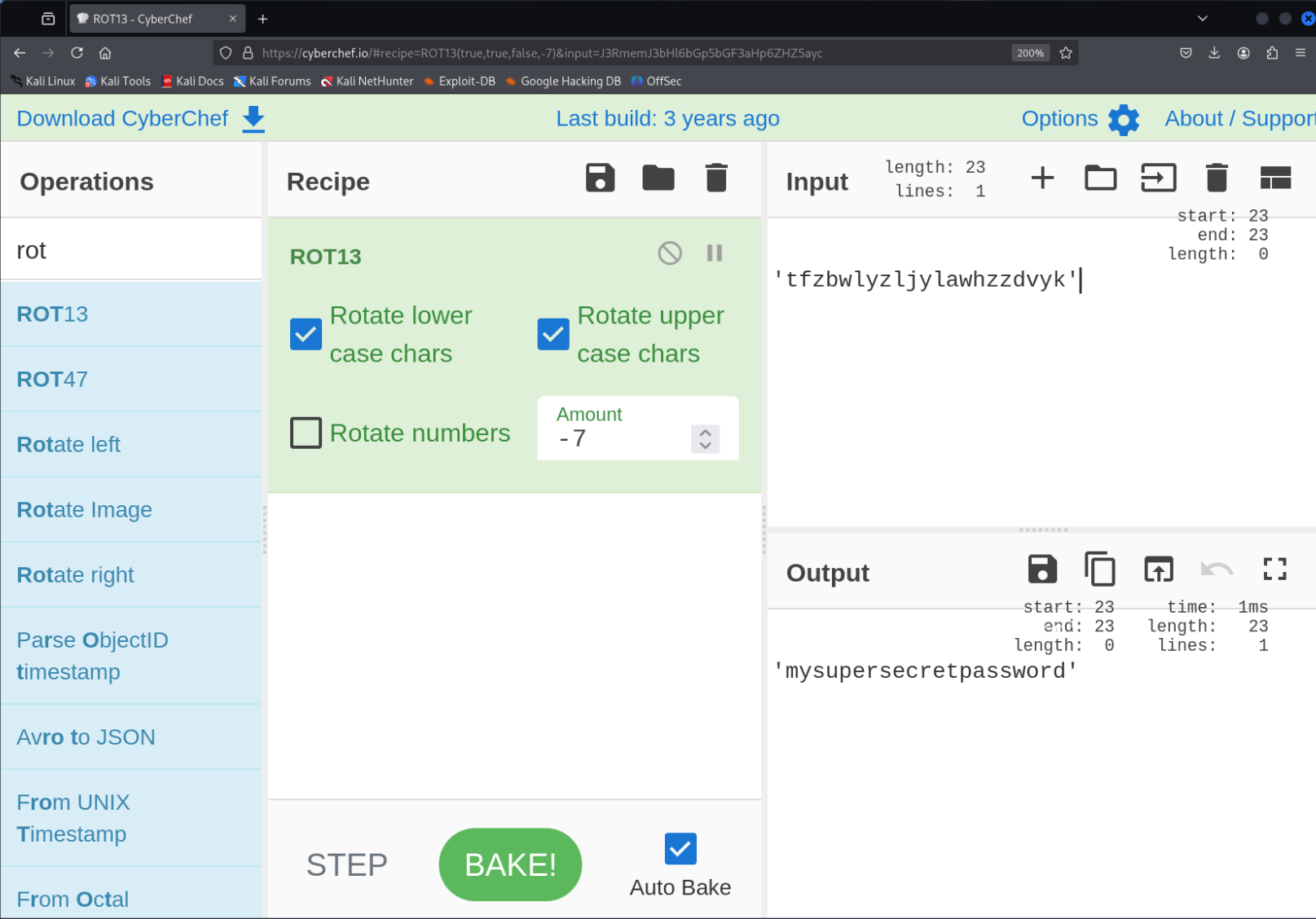
What is the password?
mysupersecretpassword
Python 3
Given a compiled Python script, find a password to authenticate the program.
Tools used
- uncompyle6
Process
- Download
PYTHON3.pyc - Run uncompyle6 (up to Python 3.12)
- The uncompiled script is here:
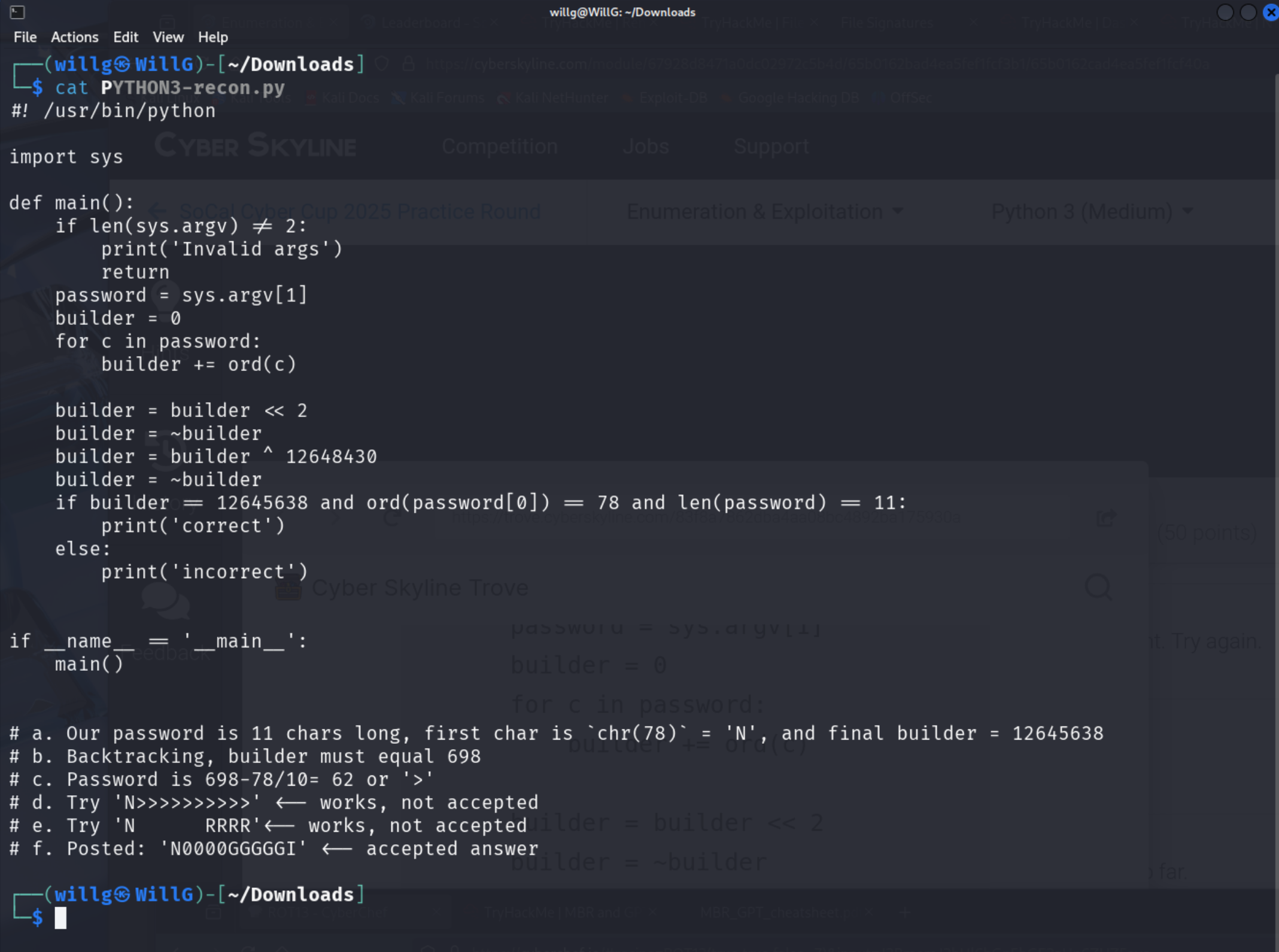
- Solve for password –> See Notes a.-f. in the image above. Analyzing the function, the length of the password is 11 characters and the first character is
ord(password[0]) == 78, or the first character ischr(78) == "N". Solving for the variable,buildermust equal 698 total. Therefor after the first character, the remaining ten characters must sum to 698 less 78 = 620. Ten>chars = 620 but this is not accepted. Four0= 4 * 48, fiveG= 5 * 71, and oneI= 1 * 73 = 620.
What is the password?
N0000GGGGGI
Binary 1
From CySky: We need to break into a program that hackers have created. You will need to provide the identifier, 7074, as the only argument to the program.
Tools used
- gdb
- Ghidra
Process
We need to use a disassembler program to access the compiled binary. Compiled binaries are machine code instructions represented in assembly language.
- Download
RE1_64bit - First pass:
- Run gdb:
gbd RE1_64bit, then at (gdb) prompt:disassemble main - From the CySky literature, note that there is a call to
gets, a known source of buffer overflow issues.
- Run gdb:
- Second pass:
- Run ghidra: go to installed directory, e.g.
cd ghidra_11.3.1_PUBLIC, then run./ghidraRun
- Run ghidra: go to installed directory, e.g.
- Open
RE1_64bitin ghidra and select analyze. The result is a decompiled source code written in C. Check out the primary function, which ismain(). - In
main(), Line 21 is asking for a password input. If the variablelocal_cis zero, the password fails, otherwise the functionfg()runs with parameterarg_v- that is, if the password is correct,fg()runs.
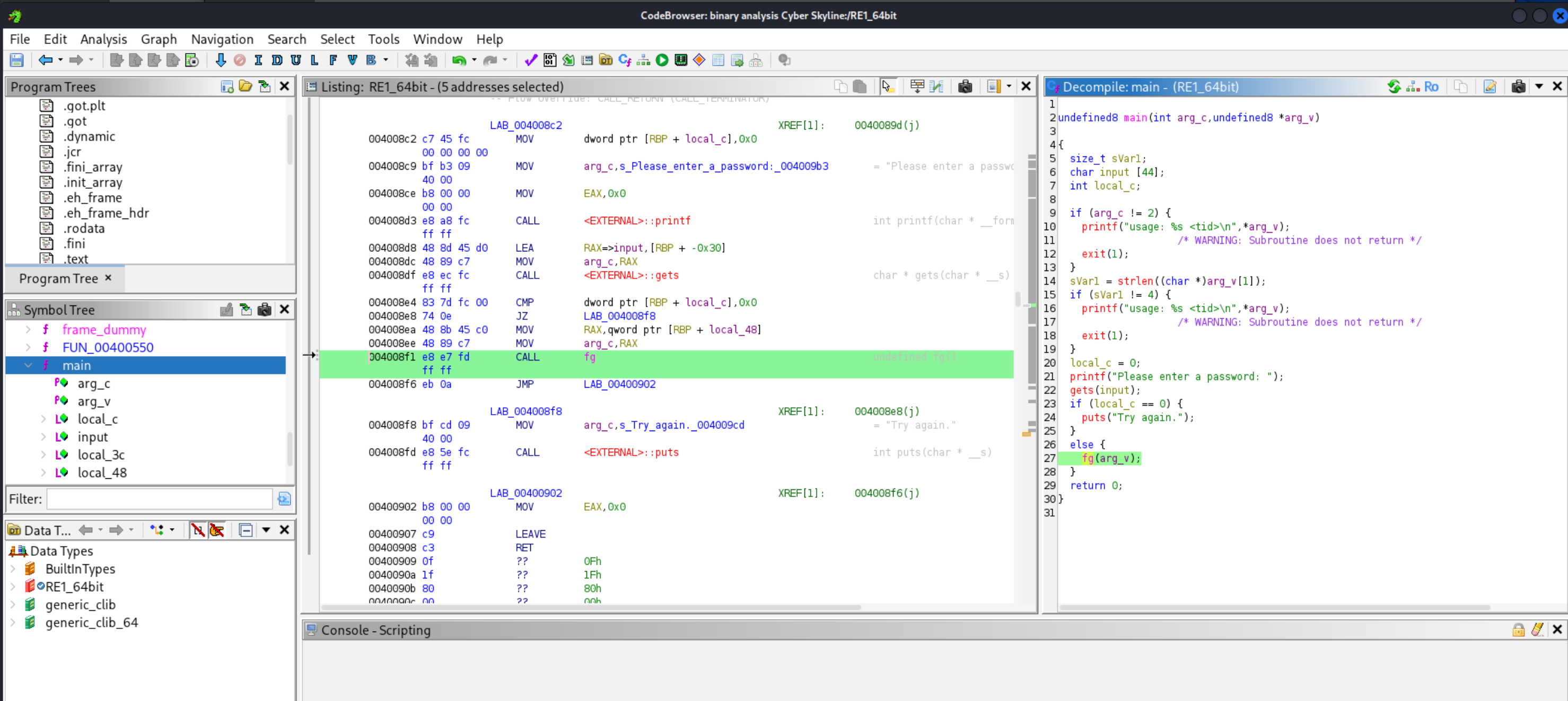
- Here we should keep in mind that we are given the ‘identifier’
7074- what does this refer to? - We need to review
fg(). We can tell that the variableslocal_1cthroughlocal_28are allcharand amount to 13 total characters, which also is the length of the flag. We also know that a flag typically has the-character at positions 3 (local25) and 8 (local20), e.g. “xxx-xxxx-xxxx”.
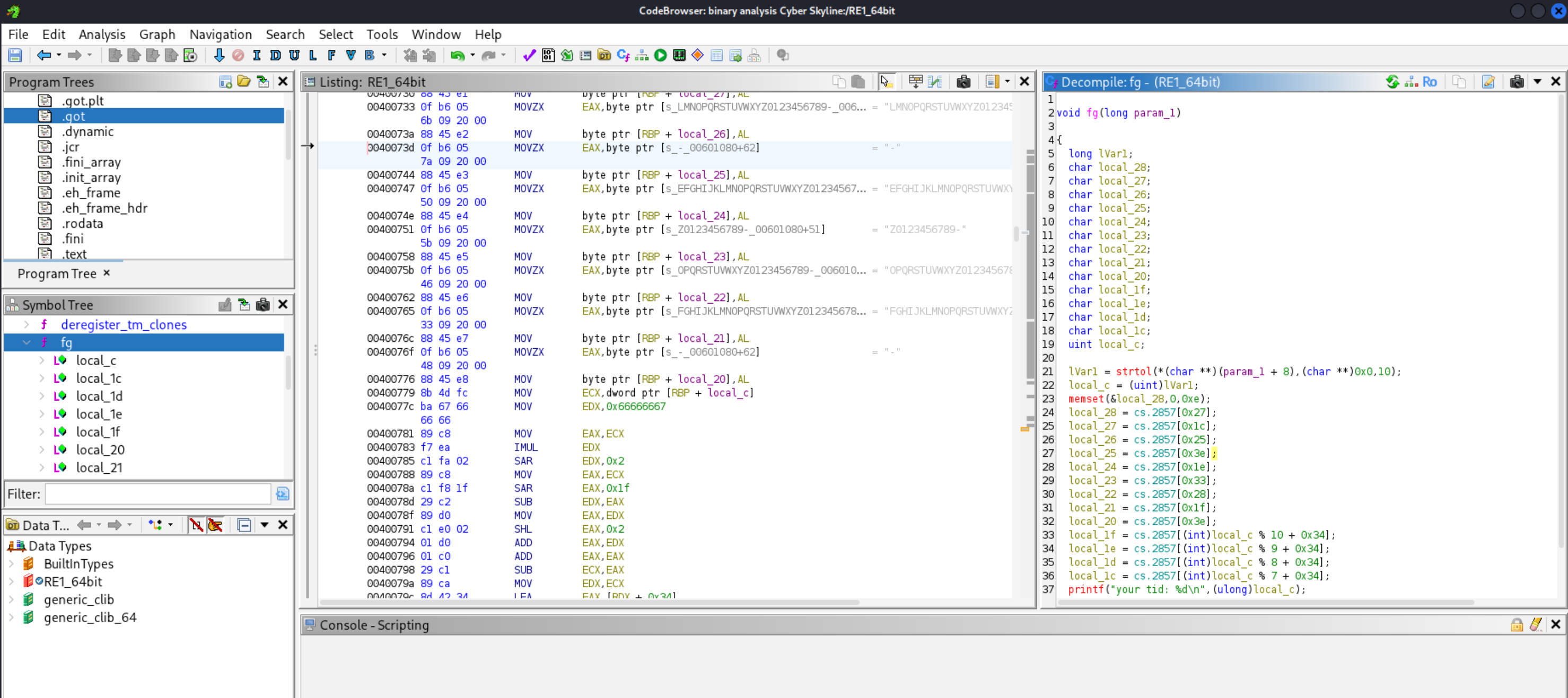
- The value of these two characters match, i.e.
cs.2857[0x3e]. This does not match an ASCII table directly- so this is not it. But if you highlightlocal_25andlocal_20separately, the first character in the string shown is-.
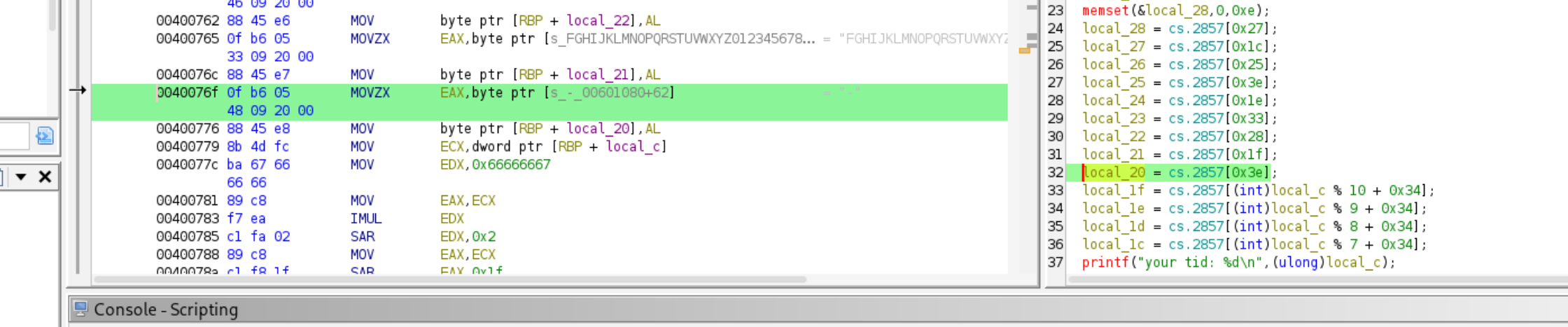
- Following this logic, the first 9 characters are:
NCL-EZOFand then four additional characters converted intoints. - If
local_c == 7074, then the next for numbers arelocal_c%10,9,8,7 =c%10 == 4,c%9 == 0,c%8 == 2andc%7 == 4or4024. - Together:
What is the flag hidden in the program?
NCL-EZOF-4024
Binary 2
From CySky: We need to break into a program that hackers have created. You will need to provide the identifier, 4930, as the only argument to the program.
Tools used
- gdb
- Ghidra
Process
We need to use a disassembler program to access the compiled binary. Compiled binaries are machine code instructions represented in assembly language.
- Download
RE2_64bit - First pass:
- Run gdb:
gbd RE2_64bit, then at (gdb) prompt:info functions(suggested by hints)
- Run gdb:
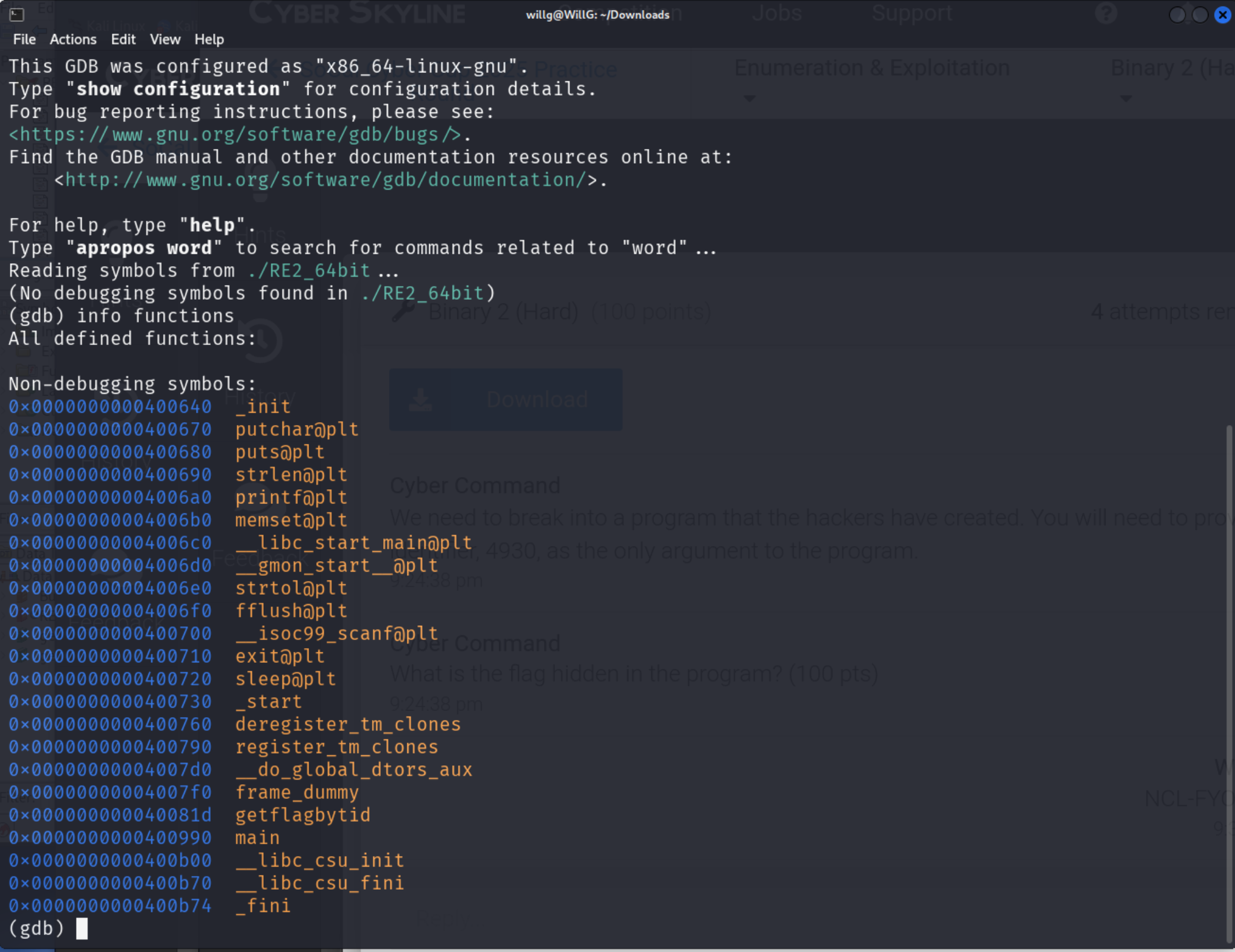
- Note the function
getflagbyid. - Also suggested by hints, run
break mainthenr, thencall (void) getflagbyid(4930) - Ultimately, no “(debugging) symbol table” found.
- There might be a way around this, but for now need to abandon this approach.
- Second pass:
- Run ghidra: go to installed directory, e.g.
cd ghidra_11.3.1_PUBLIC, then run./ghidraRun - Open
RE2_64bitin ghidra and select analyze. The result is a decompiled source code written in C. Check out the primary function, which ismain(). - [!Note that a “Symbol Tree” is shown by ghidra…]
- We can also review
getflagbyid(). Similar to Binary 1, there are 9 chars shown, with characters 3 and 8 again the same, and again this corresponds to-as seen below. There is also a stack of 4 chars, and together this matches the signature of theNCLflag.
- Run ghidra: go to installed directory, e.g.
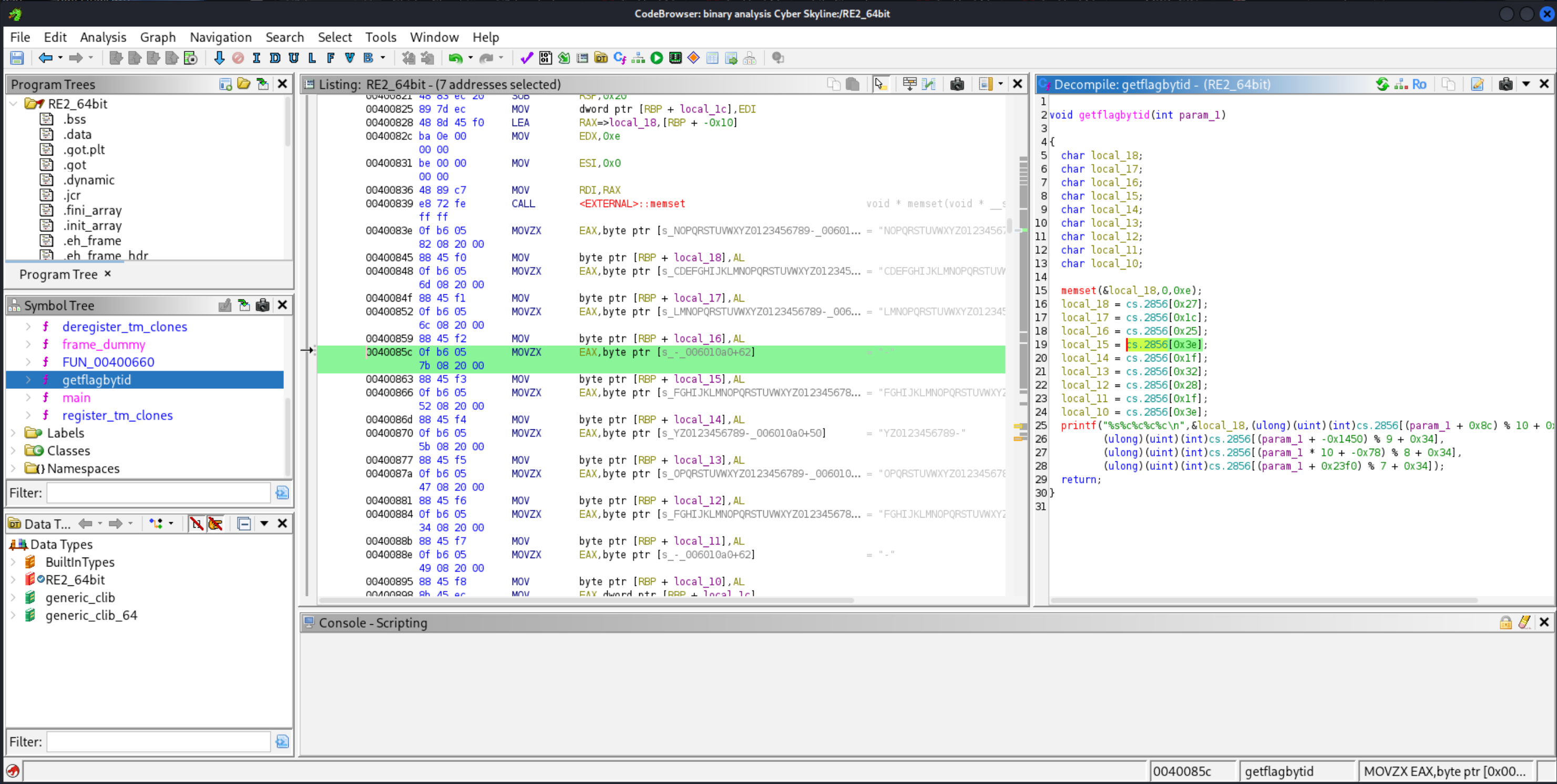
- Following this logic, the first 9 characters are:
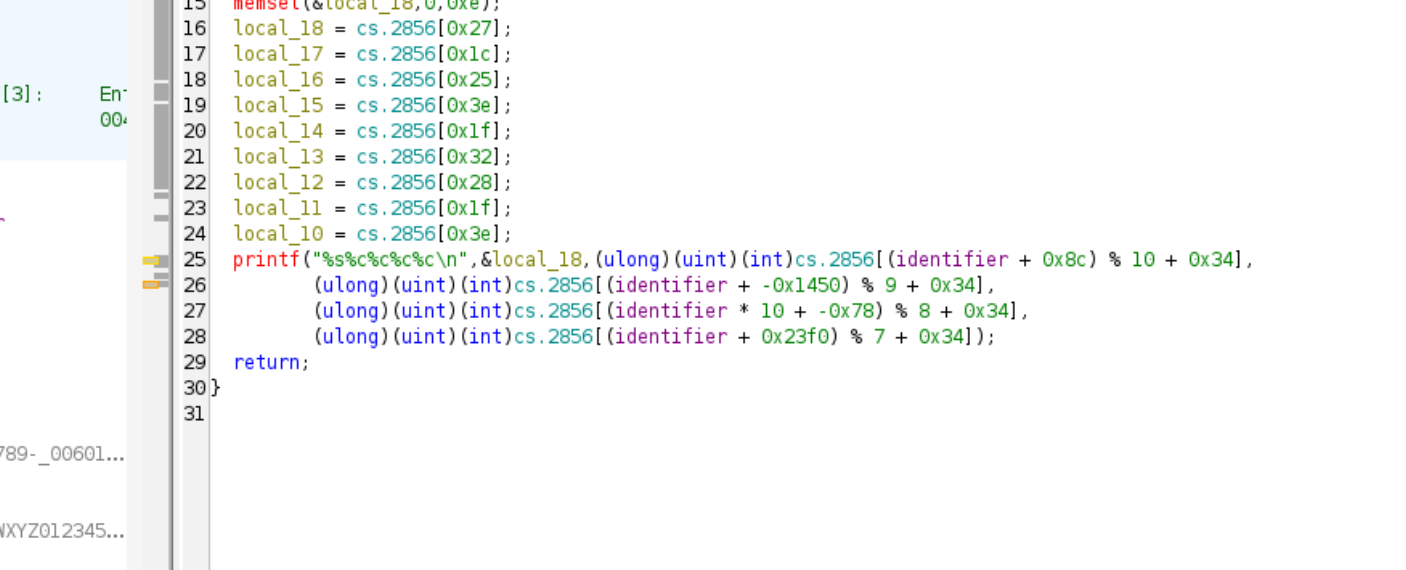
NCL-FYOFand then four additional characters converted intoints. - The last four characters are shown below.
- Given
identifier/id == 4930,- 1st:
(id + 0x8c = 140)%10 = 0 - 2nd:
(id + (-0x1450 = -5200))%9 = 0 - 3rd:
((id * 10) + (-0x78 = 120))%8 = 4 - 2nd:
(id + (0x23f0 = 9200))%7 = 4
- 1st:
- Thus, the last four characters are
0044
- Given
- Together:
What is the flag hidden in the program?
NCL-FYOF-0044
